Advanced Sleep Repair
Advanced Sleep Repair transcends traditional sleep aids, offering a complete, precision-targeted protocol focused on amplifying restorative and age-reversing processes. Recognized by experts as the ultimate tool for essential bodily repair, sleep is a cornerstone of performance and aging. But starting in your mid-20’s, your body's circadian rhythm and overnight repair mechanisms gradually decline, leading to diminished sleep quality, accelerated bodily deterioration, and cognitive decline - inflicting more harm on your body than smoking (1). Through a precision blend of L-theanine, GABA, glycine, magnesium, vitamin B6, L-tryptophan, sour cherry extract, taurine and zinc, Advanced Sleep Repair meticulously targets and corrects these deficiencies, enhancing DNA repair and metabolic balance, combats oxidative stress, fostering healthy neurotransmitter levels, and naturally fine-tuning serotonin and melatonin levels crucial for sleep-wake cycles.
Couldn't load pickup availability
As seen in
Your sleep, supercharged for longevity

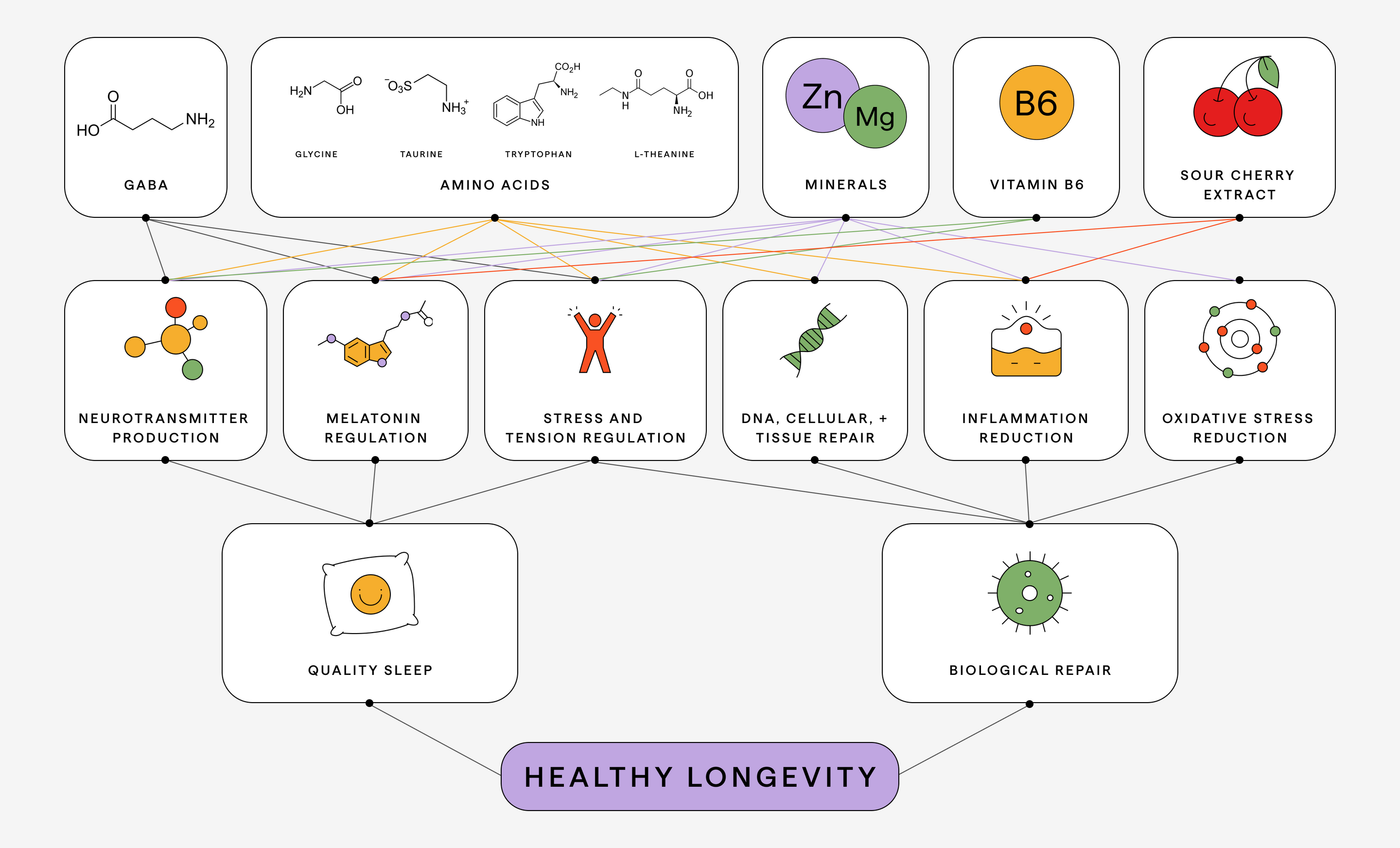
Why it’s different
-
ENGINEERED FOR SMARTER SLEEP
Quality, not quantity
-
SUPPORTS NATURAL MELATONIN PRODUCTION
COMBAT AGE-RELATED CIRCADIAN DYSREGULATION
-
OPTIMIZES NOCTURNAL DNA REPAIR
ESSENTIAL FOR CELLULAR LONGEVITY
-
DEFENDS AGAINST OXIDATIVE STRESS
REVITALIZES DAMAGE
-
FORTIFIES COGNITIVE LONGEVITY
SHARPER MENTAL PERFORMANCE, HEALTHIER BRAIN
-
IMPROVED METABOLIC HEALTH
WHILE YOU SLEEP
-
MUSCLE, SKIN, AND JOINT REJUVENATION
PROVIDES CRITICAL BUILDING BLOCKS FOR OVERNIGHT TISSUE REPAIR
-
RESTFUL SLEEP, WITHOUT DEPENDENCY
NON-SEDATIVES, SAFE FOR DAILY, LONG TERM USE
-
PROMOTES RELAXATION
HELPS REDUCES STRESS
-
BALANCED NEUROTRANSMITTERS
FOR PRECISION SLEEP & MOOD REGULATION
How to use
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new
you, like new

Look inside
-
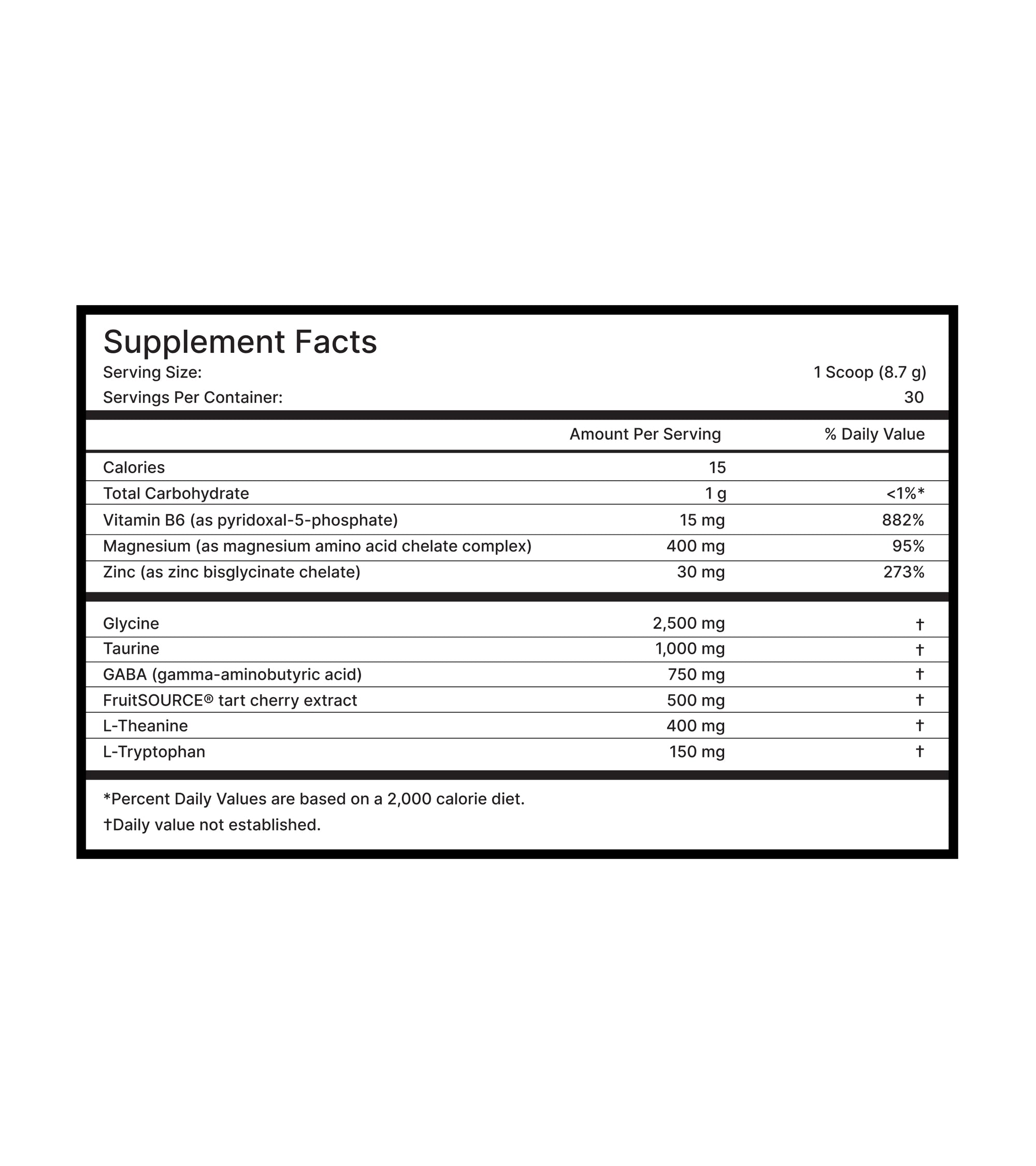
L-theanine
400 mg
L-theanine, an amino acid in tea leaves, is known for its calming effects. It enhances relaxation and sleep by increasing alpha brain waves, reducing anxiety, and promoting calmness, aiding sleep onset (55, 56). It improves deep sleep quality and reduces nighttime awakenings, benefiting mood and cognitive function. L-theanine appears to extend lifespan in some organisms by upregulating aging-protective proteins and antioxidative enzymes, aiding in managing glycation-induced crosslinks (74). It also boosts cognitive functions like focus and attention, particularly under stress (30). To get 400mg in our formula, you would need to drink 20 cups of green tea.
-
GABA
750 mg
GABA, a brain neurotransmitter, is key in regulating neuronal excitability and promoting relaxation. As an inhibitory neurotransmitter, it helps calm the mind. Studies show its potential in improving sleep quality and reducing insomnia. By binding to brain receptors, GABA reduces neuronal activity, aiding in falling and staying asleep. Supplementation may enhance sleep duration, shorten sleep onset time, and improve sleep quality. It also helps reduce anxiety and stress, which often disrupt sleep (60, 76). Trace amounts of GABA are present in soya products, fermented foods, and green tea.
-
Glycine
2,500 mg
Glycine, a non-essential amino acid, improves sleep quality by reducing sleep latency and enhancing sleep efficiency (77, 78). It helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle and has been shown to extend lifespan in various organisms, including multiple mammalian models. Glycine improves health in mammalian models of age-related diseases. It acts as an acceptor for Glycine N-methyltransferase, crucial for methionine clearance. Glycine's conversion to sarcosine has been known to induce autophagy, mimicking methionine restriction efforts, potentially aiding in longevity (37, 41). Its role in these biochemical pathways makes glycine beneficial for healthy lifespan extension.
-
Magnesium (amino acid chelate complex)
400 mg
Magnesium is a vital mineral that aids sleep regulation by activating the parasympathetic nervous system for relaxation and stress reduction. It assists in managing neurotransmitters and hormones like melatonin and GABA essential for sleep (62, 63, 80). Research suggests that magnesium supplementation can enhance sleep quality, lessen insomnia symptoms, boost sleep efficiency, and alleviate restless leg syndrome. Furthermore, magnesium promotes genomic stability, heart health, balanced blood sugar levels, and a healthy inflammatory response (43, 80). We leverage a chelated magnesium amino acid complex, among the most bioavailable and diverse forms of magnesium to help ensure superior absorption.
-
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxal-5-phosphate)
15 mg
Vitamin B6, as pyridoxal-5-phosphate, is crucial for numerous biochemical processes, including sleep health. It aids in synthesizing neurotransmitters like serotonin and GABA, vital for sleep regulation and relaxation (81). By facilitating L-tryptophan's conversion to serotonin, a precursor to the sleep-regulating hormone melatonin, it helps maintain healthy sleep patterns (12). When combined with magnesium, the effectiveness of pyridoxal-5-phosphate is enhanced. Magnesium activates vitamin B6 into its functional form, pyridoxal-5-phosphate, and together they improve neurotransmitter function and sleep quality (42, 82). To get the amount of Vitamin b6 found in Advanced Sleep Repair, you would have to consume around 1.7 kg of canned tuna.
-
Taurine
1,000 mg
Taurine, a naturally occurring amino acid found in the body, contributes to better sleep, combats oxidative stress, and potentially supports longevity. As a neuromodulator, it promotes relaxation and calmness, aiding restful sleep (72). Its antioxidant properties protect cells from damage linked to chronic diseases and aging, potentially contributing to longevity by preserving cellular health (24, 83). Studies show oral taurine supplementation in middle-aged mice significantly extended lifespan by 10-12% and improved life expectancy and organ function, including bone, muscle, pancreas, brain, fat, gut, and immune system (21). To get the equivalent amount of taurine present in Advanced Sleep Repair you would need to eat 2kg (4.4 pounds) of chicken breast.
-
L-Tryptophan
150 mg
An essential amino acid that serves as a precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter involved in regulating mood and sleep. L-Tryptophan has been studied for its potential sleep-enhancing effects, particularly in improving sleep latency (time taken to fall asleep) and sleep quality. By increasing serotonin and melatonin levels in the brain, L-tryptophan can help promote relaxation and contribute to more restful sleep (84, 85). L-tryptophan can be found in turkey and pumpkin seeds.
-
Tart Cherry Extract
500 mg
Tart cherry (Prunus cerasus) extract contains natural melatonin, key for regulating sleep-wake cycles and maintaining healthy sleep patterns. Studies show that tart cherry supplementation can boost melatonin levels, enhancing sleep quality, duration, and efficiency, while reducing insomnia symptoms and easing jet lag. Its natural melatonin makes it an effective option for natural sleep support (14, 86). Tart cherry extract is regularly used by elite athletes, as it may aid muscle regeneration, thanks to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (87).
-
Zinc
30 mg
It is an essential mineral that plays a role in numerous physiological processes, including sleep regulation. It synthesizes and metabolizes neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and melatonin, which are crucial for maintaining healthy sleep patterns. Zinc deficiency has been associated with sleep disturbances and insomnia. Supplementing with zinc may help improve sleep quality, reduce nighttime awakenings, and enhance overall sleep efficiency (88, 89).
How can sleep impact longevity?
Learn more
Sleep is the single most effective thing we can do to reset our brain and body health each day: Mother Nature's best effort yet at contra-death
Matthew Walker, Author of Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and Dreams
Scientific studiеs
-
The effects of taking glycine (3 g) before bedtime were examined in a study on individuals with unsatisfactory sleep. The results showed that glycine improved subjective sleep quality and efficacy (sleep time divided by time spent in bed). It also reduced the time to fall asleep and reach slow-wave sleep without affecting the overall sleep architecture. Additionally, glycine reduced daytime sleepiness and enhanced performance in memory recognition tasks. These findings suggest that when ingested before bedtime, glycine can improve subjective and objective measures of sleep quality in a manner different from traditional hypnotic drugs like benzodiazepines (90).
-
The effects of Bioglycin, a form of glycine that interacts with the N-methyl D-aspartate receptor complex, were studied in young and middle-aged individuals to assess attention, memory, and mood. In a double-blind, randomized, crossover study, healthy students (mean age, 20.7 years) and middle-aged men (mean age, 58.9 years) were tested. The middle-aged group showed poorer verbal episodic memory, attention, and subjective responses compared to the young group. Bioglycin improved episodic memory in both groups and enhanced sustained attention in middle-aged men. Unlike other cognitive enhancers, Bioglycin lacked stimulant properties, had no significant effects on mood, and primarily improved memory rather than attention. It may be beneficial for situations requiring high retrieval of information or when performance is affected by factors like jet lag, shift work, or disrupted sleep (29).
-
The simple amino acid glycine extends lifespan in worms, mice, and rats. Glycine also improves aspects of health in mammalian models of age-related disease. Glycine is the acceptor for GNMT, an enzyme responsible for methionine clearance. GNMT also converts glycine to sarcosine, an autophagy-inducing metabolite. Glycine may prolong life by inducing autophagy and mimicking methionine restriction.
-
Slowing brain aging is crucial for preventing dementia, as aging is the primary risk factor. Green tea catechins (GTCs) have potent antioxidant activity and can reduce oxidative damage, brain atrophy, and cognitive decline in aged mice. Ingesting GTCs or drinking green tea at a middle-aged stage can suppress age-related cognitive decline. Chronic stress accelerates brain aging, but L-theanine, an amino acid in green tea, can mitigate stress-induced aging. Regular consumption of green tea is beneficial in slowing brain aging, and theanine-rich green tea or low-caffeine green tea may help suppress stress and stress-induced aging (93).
-
The study investigated the protective effect of L-theanine against irinotecan-induced DNA damage in mouse bone marrow cells. L-theanine, given at doses equivalent to 30 or 60 mg/kg for 12 days, showed no genotoxic or cytotoxic effects. Pretreatment with L-theanine reduced irinotecan-induced genomic damage in bone marrow cells in a dose-dependent manner. Irinotecan caused oxidative DNA stress, but L-theanine administration mitigated these effects by modulating cellular antioxidant levels. The findings suggest that L-theanine has a protective role in preventing irinotecan-induced DNA damage in mouse bone marrow cells (94).
-
The GABA/L-theanine mixture decreased sleep latency and increased sleep duration compared to GABA or L-theanine alone. REM and NREM sleep were significantly increased with the combination, indicating improved sleep quality. The mixture restored normal sleep time and quality in an animal model of caffeine-induced awareness. The increased expression of GABA and the glutamate GluN1 receptor subunit suggests that the GABA/L-theanine combination has neuromodulatory effects on sleep behavior (61).
-
Magnesium is an essential element involved in various metabolic pathways and plays a crucial role in maintaining genomic stability. It is not genotoxic and helps stabilize DNA and chromatin structure. Magnesium serves as a cofactor in enzymatic systems responsible for DNA processing, ensuring high fidelity during DNA replication and facilitating DNA damage repair. Intracellular magnesium levels are tightly regulated and contribute to cell cycle control and apoptosis. Magnesium deficiency can affect membrane integrity, increase susceptibility to oxidative stress, and be linked to cardiovascular diseases and accelerated aging. The relationship between magnesium and tumor formation is complex, as it may have protective effects at early stages but promote tumor growth later on. Marginal magnesium deficiencies are common due to inadequate daily intake in many industrialized countries, falling below recommended dietary allowances (17).
-
This study aimed to assess the impact of four-week magnesium supplementation on DNA integrity in individuals with sedentary lifestyles and rugby players. Sedentary lifestyle is associated with increased risks of cardiovascular disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes, while strenuous exercise can induce oxidative stress and DNA damage. Using the comet assay, the study found that rugby players had significantly higher levels of DNA damage in peripheral blood lymphocytes compared to sedentary students. However, magnesium supplementation reduced the number of cells with high DNA damage in both groups when exposed to H2O2, and in rugby players, it also reduced the number of cells with medium DNA damage. These findings suggest that four-week magnesium supplementation can protect DNA from oxidative damage in both sedentary individuals and rugby players (95).
-
Taurine, a semi-essential micronutrient abundant in humans and other eukaryotes, emerges as a potential influencer in the aging process. Research indicates that taurine levels in the blood decrease with age in various species, including mice, monkeys, and humans. Notably, administering taurine orally to middle-aged C57Bl/6J mice led to a visible extension in their median lifespan by 10 to 12% and an increase in life expectancy at 28 months by approximately 18 to 25%. This treatment also significantly enhanced their overall health, as evidenced by improved organ functionality. Similar benefits in health span were observed in monkeys. While taurine's impact was not significant in unicellular yeast, it did extend the lifespan of multicellular worms. The supplementation of taurine positively influenced several critical aspects of aging, such as reducing cellular aging, defending against deficiencies in telomerase, lessening mitochondrial dysfunction, curbing DNA damage, and diminishing inflammation. In humans, lower levels of taurine and related compounds correlate with various health problems, including obesity, hypertension, inflammation, and diabetes. Additionally, exercise was found to elevate levels of taurine metabolites, potentially linking physical activity's anti-aging benefits to taurine (21).
-
This study aimed to assess the effect of L-tryptophan (Trp) supplementation on sleep quality by analyzing existing research through a meta-analysis. Sleep disturbances have been linked to various health conditions, so understanding the impact of Trp on sleep is essential. A total of 18 articles were collected and analyzed for sleep outcomes such as total sleep time, sleep latency, wake after sleep onset and sleep efficiency. The results indicated that Trp supplementation can reduce wake-after-sleep onset (WASO). The analysis also revealed that a Trp dose of at least 1g was more effective in lowering WASO compared to a dose below 1g. However, Trp supplementation did not show significant effects on other sleep components. In conclusion, Trp supplementation, particularly at 1g or more doses, can help improve sleep quality (15).
Your personal longevity kit, engineered for life
More than just a supplement, each product is a complete protocol and lifestyle program, synergistically formulated to work best together, and with ongoing use.
One-Time Purchase
Receive a pouch filled with a one month supply of any product
Subscribe to unlock VIP benefits
Your welcome kit includes a free storage canister to store your monthly delivery. 100% metal and recyclable, for you, and for the planet
+ Free coaching and scientific guidance, delivered straight to your inbox
+ Up to 30% off subscriptions, cancel anytime
+ White glove, subscribers-only access to the team for questions on your longevity protocol
+ Constantly updated formulas that track the latest science, so you don’t have to
+ First in line benefits for new products, special discounts, and features
Here's what our customers say
-
Feeling unstoppable
I forgot what it felt like to feel energized. I was so overrun with fatigue for many years that I just got used to it but once I started taking Jung, I began to feel more alert, have stronger performance both mentally and physically, and my mood elevated as well. In the gym, I was instantly able to lift more weights and feel that I was able to perform sprints more easily. I recover more quickly from the hard training that I do and overall, I feel fantastic!
-
Youth in a pill
Makes me feel amazing!
-
I feel like I have gotten younger
I simply feel like I have more energy to do everything. This is like a caffeine jolt without any of the side effects. I am hoping these results continue and build on what is currently happening? I'm willing to continue for a couple of months to find out.
FAQ’s
-
What is Advanced Sleep Repair?
-
How does Advanced Sleep Repair work?
-
How should I take Advanced Sleep Repair?
-
Is Advanced Sleep Repair suitable for everyone?
-
Can I become dependent on Advanced Sleep Repair for sleep?
-
How long does it take for Advanced Sleep Repair to work?
-
How can I enhance the effectiveness of Advanced Sleep Repair?
-
I experience excessive overnight urination, and I'm concerned that drinking a cup of this product will disturb my sleep. What should I do?
100% Money Back Guarantee
At Jung, we believe in the power of our products and want you to feel confident in your purchase. That’s why we’ve partnered with Onward to offer an unmatched money-back guarantee. With Onward VIP Protection, your purchase is covered by a full money-back guarantee. If you’re not completely satisfied, simply return the product for a hassle-free refund.
100% Money Back Guarantee
Pairs well with Longevity Foundation
Jung+ boosters have been precision engineered to work synergistically with our Master Formula. Combine your booster with Longevity Foundation to create a complete longevity protocol that targets aging at the cellular level, and goes further to turbocharge your health goals and amplify your unique lifestyle.


Longevity Foundation
Welcome to the future of anti-aging. Devised by world-leading longevity experts, our foundational formula works around the clock to tackle aging at its roots, addressing all 12 known drivers of aging with precision.
















References
-
Reference link
1. Baugh A, Buhr RG, Quibrera P, Barjaktarevic I, Barr RG, Bowler R, et al. Risk of COPD exacerbation is increased by poor sleep quality and modified by social adversity. Sleep. 2022;45(8).
-
Reference link
2. Libman E, Fichten C, Creti L, Conrod K, Tran D-L, Grad R, et al. Refreshing sleep and sleep continuity determine perceived sleep quality. Sleep Disorders. 2016;2016.
-
Reference link
3. Reed DL, Sacco WP. Measuring sleep efficiency: what should the denominator be? Journal of clinical sleep medicine. 2016;12(2):263-6.
-
Reference link
4. Fuller PM, Gooley JJ, Saper CB. Neurobiology of the sleep-wake cycle: sleep architecture, circadian regulation, and regulatory feedback. Journal of biological rhythms. 2006;21(6):482-93.
-
Reference link
5. Cornwall W. Deep sleep. American Association for the Advancement of Science; 2015.
-
Reference link
6. Brzezinski A, Vangel MG, Wurtman RJ, Norrie G, Zhdanova I, Ben-Shushan A, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on sleep: a meta-analysis. Sleep medicine reviews. 2005;9(1):41-50.
-
Reference link
7. Zhdanova IV, Lynch HJ, Wurtman RJ. Melatonin: a sleep-promoting hormone. Sleep. 1997;20(10):899-907.
-
Reference link
8. Dawson D, Encel N. Melatonin and sleep in humans. Journal of pineal research. 1993;15(1):1-12.
-
Reference link
9. Ma L, Liu Q, Tian M, Tian X, Gao L. Mechanisms of melatonin in anti-aging and its regulation effects in radiation-induced premature senescence. Radiation Medicine and Protection. 2021;2(1):33-7.
-
Reference link
10. Anisimov VN, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Anisimov SV, Vesnushkin GM, Vinogradova IA. Melatonin as antioxidant, geroprotector and anticarcinogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1757(5-6):573-89.